Can the Pneumococcal Vaccine Cause Injury and/or Death?

IMPORTANT NOTE: Corvelva invites you to get in-depth information by reading all the sections and links, as well as the manufacturer's product leaflets and technical data sheets, and to speak with one or more trusted professionals before deciding to vaccinate yourself or your child. This information is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice.
The problem of multiple vaccines (click to open)
The problem of multiple vaccines

The current vaccination calendars, especially for the pediatric age, provide for the administration of multiple antigens and vaccines in a single session, favoring comfort at the expense of safety. In order to be able to make a specific speech on the safety of vaccines, we must necessarily take into consideration the complexity of the phenomenon, advising all readers to adequately inform themselves on all aspects of vaccination, pros and cons.
Dr. Russell Blaylock, clinical assistant professor of neurosurgery at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, has studied "toxic synergy" for years and was able to observe that when two weakly toxic pesticides, where neither is able to cause Parkinson's syndrome in experimental animals, are combined with each other, can cause the disease even quickly and compares this phenomenon to that of multiple vaccines administered simultaneously: "Vaccinations, if too numerous and too close together, behave like a disease chronic".(a). Others Two studies have confirmed that sudden infant death can occur after inoculation of multiple vaccines in a single administration.(bc)
A study published in Human and Experimental Toxicology showed that countries that prescribe more vaccines in children tend to have higher infant mortality rates.(D) For example, in the United States, where children receive 26 vaccines, more than 6 children per 1000 live births die, while in Sweden and Japan, where 12 pediatric vaccines are administered, 3 deaths are reported for every 1000 live births. In the aforementioned study, the link between vaccines and SIDS is also considered.
From a Swiss study published in 2005 in the European Journal of Pediatrics(E) it results that, regarding the effects on preterm infants, the incidence of recurrent or increased apnea and bradycardia after administration of hexavalent vaccines is 13%. That same year, the same journal published a German study that had examined sudden infant deaths after hexavalent. The authors write: «These results, based on spontaneous reports, do not prove a causal relationship between vaccination and sudden infant death, but constitute a signal regarding one of the two available hexavalents; signal that should lead to intensify surveillance of sudden infant deaths after vaccination".(f)
In 2006, it was published in the medical journal Vaccine(g) the letter from a team of researchers from the University of Munich which reported «six cases of sudden infant death after hexavalent vaccination.. All found dead without explanation 1-2 days after vaccination». They had been classified as typical cases of sudden infant death but the autoptic verification had revealed neuropathological and histological abnormalities and all the children showed a significant cerebral edema which made them an exception compared to the other SIDS cases (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome). The researchers wrote that “Before the introduction of the hexavalent vaccine (in the years 1994-2000), we had observed the case of only one in 198 children with sudden infant death who died soon after the DTP vaccination. But between 2001 and 2004 they had identified five similar cases out of 74 with SIDS. That would indicate a thirteen-fold increase."
Also in 2006 on Virchows Archive(H), the team from the Institute of Pathology of the University of Milan wrote: «Experts from the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medical Products have analyzed the possibility that there could be a link between hexavalent vaccines and some cases of death. Participants included pathologists with experience in vaccines and sudden infant death syndrome who conducted the autopsies. But, as far as we know, little attention was paid to examination of the brainstem and blood heart on serial sections and there was no possibility of establishing a trigger role of the vaccine for these deaths. Here we report the case of a 3-month-old girl who died suddenly after hexavalent vaccination. Examination of the brain stem on serial sections revealed bilateral arcuate nucleus hypoplasia. The conduction system of the heart had persistent fetal dispersion and degeneration. This case offers a unique understanding of the possible role of the hexavalent vaccine in triggering a lethal consequence in a vulnerable child. Any case of sudden and unexpected death that occurs soon after birth or in early childhood, especially if following a vaccination, should always undergo a full necropsy, according to guidelines.
References
- Blaylock R, "Vaccinations: the hidden dangers", The Blaylock Wellness Report, May 2004, pp.1-9
- Ottaviani G. et al., "Sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) shortly after hexavalent vaccination: another pathology in suspected SIDS?", Virchows Archiv., 2006, 448, pp. 100-104.
- Zinka B. et al., "Unexplained cases of sudden infant death shortly after hexavalent vaccination", Vaccine, July 2006, 24 (31-32), pp. 5779-5780.
- Miller NZ et al1. , "Infant mortality rates regressed against number of vaccine doses routinely given: there is a biochemical or synergistic toxicity?", Hum. Exp. Toxicol., May 2011.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15843978/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15602672/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15908063/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16231176/
The aluminum problem (click to open)
Aluminum in vaccines: what parents need to know

1. What is aluminum?
Aluminum is a silvery-white light metal, malleable and resistant. These qualities make it useful in numerous industries and products, including machinery, construction, warehouses, cookware, kitchen utensils, textiles, dyes and cosmetics. Aluminum is also the most abundant metal in the earth's crust, and virtually all of the aluminum in the environment is found in the soil. However, aluminum is not found naturally in significant quantities in living organisms (such as plants and animals) and has no known biological function. Over the past century, the use of aluminum in some products has led to increased human exposure. The major sources of exposure are aluminum-containing foods (e.g., baking powder, processed foods, baby formulas, etc.), medical products (e.g., antiperspirants, antacids, etc.), allergy injections, and vaccines .1-3
2. Why is aluminum present in vaccines?
Some vaccines use aluminum compounds (aluminum hydroxide and aluminum phosphate) as adjuvants, which are ingredients that increase the immune response to an antigen (foreign substance).4-5 The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) says that if some vaccines did not include aluminum, the immune response they trigger could decrease.6
3. Which vaccines contain aluminum?
The following vaccines contain aluminum and are given to infants, children and adolescents (Fig. 1):
- Hepatitis B (HepB)
- hexavalent
- Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTaP and Tdap)
- Haemophilus influenzae type b (PedvaxHIB)
- Pneumococcus (PCV)
- Hepatitis A (HepA)
- Papillomavirus virus (HPV)
- Meningococcus B (MenB)
Figure 1: Up to 18 doses of aluminum-containing vaccines are administered from birth to age 227-8
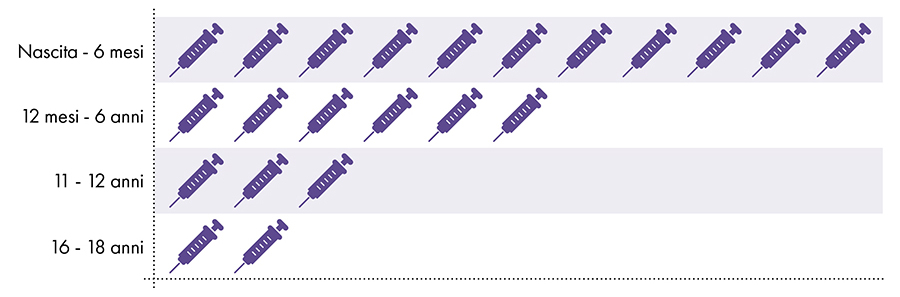
4. Is exposure to aluminum safe?
The FDA has considered aluminum generally recognized as safe (GRAS) since 1975.9 However, prior to 1990, there was no technology to accurately detect small amounts of aluminum administered to subjects in scientific studies.10 Consequently, the amount of aluminum that could be absorbed before the onset of adverse effects was not known.
Since the 1990s, thanks to technological advances, it has been observed that the small amounts of aluminum that remain in the human body interfere with a number of cellular and metabolic processes in the nervous system and tissues of other parts of the body.1-10-11 The greatest negative effects of aluminum have been observed in the nervous system and range from impaired motor skills to encephalopathy (altered mental status, personality changes, thinking difficulties, memory loss, seizures, coma and more).2-12
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) recognizes aluminum as a known neurotoxin.2 Additionally, the FDA has warned about the risks of aluminum toxicity in infants and children.13
FEDERAL REGISTER: The daily newspaper of the United States government"Even full-term infants with normal kidney function may be at risk due to rapid growth and immaturity of the brain and skeleton, as well as immaturity of the blood-brain barrier. Up to the age of 1 or 2, infants have a lower glomerular filtration rate than adults, which affects their kidney function. The agency fears that young children and those with immature kidney function are at increased risk of aluminum exposure. " |
5. How much oral aluminum is not safe?
In 2008, the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR), a division of HHS, used studies on the neurotoxic effects of aluminum to determine that no more than 1 milligram (1.000 micrograms) of aluminum per kilogram of body weight per day to avoid the negative effects of aluminum.2
6. How much aluminum injected is not safe?
To determine the amount of aluminum that can be safely injected it is necessary to convert the oral aluminum limit of the ATSDR. The ATSDR limit for oral aluminum (1.000 micrograms of aluminum per kilogram of body weight per day) is based on 0,1% of the oral aluminum that is absorbed into the bloodstream, as the digestive tract blocks almost all of the oral aluminum .2 In contrast, aluminum injected intramuscularly bypasses the digestive tract and 100% of the aluminum can be absorbed into the bloodstream over time (i.e., the proportion of aluminum absorbed is 1.000 times greater). To account for these different amounts of absorption, the oral aluminum limit of the ATSDR must be divided by 1000. This conversion leads to an ATSDR-derived blood aluminum limit of 1 microgram of aluminum (0,1% of 1.000 micrograms) per kilogram of body weight per day. Consequently, to avoid the neurotoxic effects of aluminum, no more than 1 microgram of aluminum per kilogram of body weight should enter the bloodstream on a daily basis. Figure 3 shows the ATSDR-derived blood aluminum limit for infants of various ages based on their weight.
7. How much aluminum is there in vaccines?
The amount of aluminum in vaccines varies.16 In 1968, the US federal government set the limit for the amount of aluminum in vaccines at 850 micrograms per dose, based on the amount of aluminum needed to make some vaccines effective.6-17 Consequently, the amount of aluminum in aluminum-containing infant vaccines ranges from 125 to 850 micrograms per dose. Figure 4 shows the aluminum content of one dose of various vaccines given to children.
8. Have any studies compared the amount of aluminum in vaccines with the limit derived from the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR)?
In 2011, a study was published that aimed to compare the amount of aluminum in vaccines with the blood flow limit set by the ATSDR.18 However, this study incorrectly based its calculations on 0,78% oral aluminum absorbed into the bloodstream, rather than the 0,1% value used by the ATSDR in its calculations.19-20 As a result, the 2011 study hypothesized that nearly 8 times (0,78% / 0,1%) aluminum can safely enter the bloodstream, and this has led to an incorrect conclusion.
9. Is aluminum exposure from vaccines safe?
Vaccines are injected intramuscularly, and the rate at which aluminum from vaccines migrates from human muscle into the bloodstream is unknown. Animal studies suggest that aluminum from vaccines can take anywhere from a couple of months to more than a year to enter the bloodstream, due to multiple variables.21-23 Since cumulative aluminum exposure from vaccines in children under one year of age exceeds the daily limit set by the ATSDR by several hundred (Fig. 3 and 4), the limit would still be exceeded if aluminum from vaccines entered the blood flow over the course of about a year. In addition, studies have shown that aluminum from vaccines is absorbed by immune cells and reaches parts of the body far from the injection site, including the brain.24
The extent of the adverse effects of aluminum in vaccines is not known, as safety studies have not been conducted comparing a population vaccinated with aluminum-containing vaccines with a population not vaccinated with such vaccines.
Aluminum limitation of blood flow derived from the ATSDR2-14-15
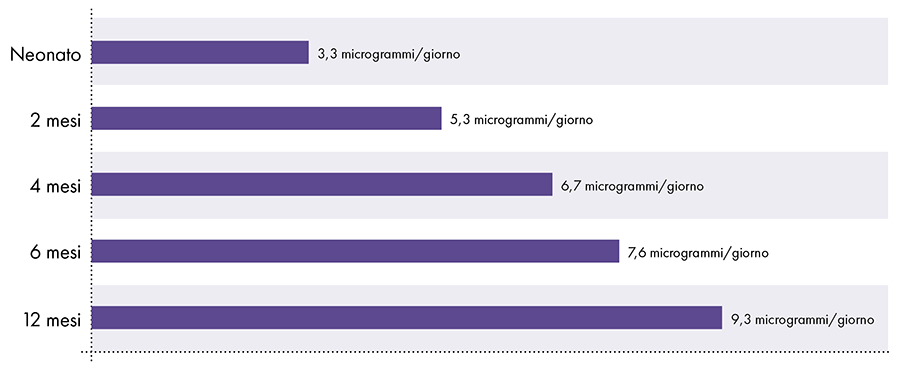 Figure 3: This graph shows the aluminum limit for children of various ages, as derived from the Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, a division of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The limit indicates that no more than 1 microgram of aluminum per kilogram of body weight should enter the bloodstream on a daily basis to avoid the neurotoxic effects of aluminum.
Figure 3: This graph shows the aluminum limit for children of various ages, as derived from the Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, a division of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. The limit indicates that no more than 1 microgram of aluminum per kilogram of body weight should enter the bloodstream on a daily basis to avoid the neurotoxic effects of aluminum.
Amount of aluminum in vaccines
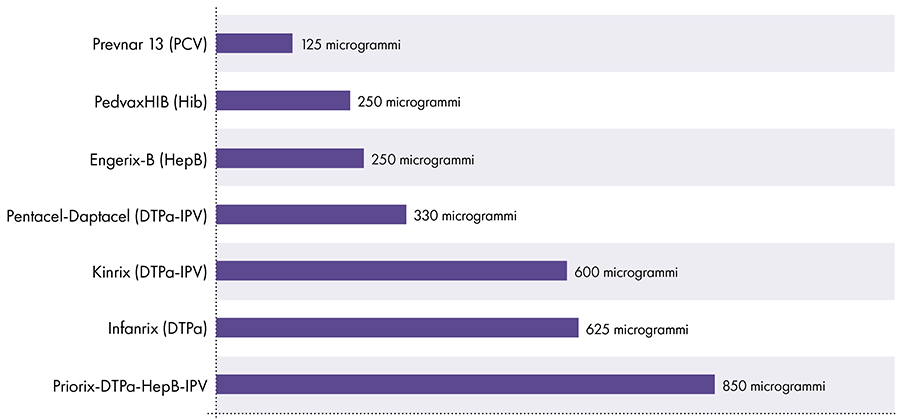
References
- American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Nutrition. Aluminum toxicity in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1996 Mar; 97 (3): 413.
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological profile for aluminum. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2008.3, 13-24, 145, 171-7, 208.
- Yokel RA. Aluminum in food — the nature and contribution of food additives. In: El-Samragy Y, editor. Food additive. Rijeka (Croatia): InTech; 2012. 203-28.
- Marrack P, McKee AS, Munks MW. Towards an understanding of the adjuvant action of aluminum. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009 Apr; 9 (4): 287.
- Volk VK, Bunney WE. Diphtheria immunization with fluid toxoid and alum-precipitated toxoid. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1942 Jul; 32 (7): 690-9.
- Baylor NW, Egan W, Richman P. Aluminum salts in vaccines — US perspective. Vaccine. 2002 May 31; 20 Suppl 3: S18-22.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Silver Spring (MD): US Food and Drug Administration. Vaccines licensed for use in the United States; [updated 2018 Feb 14; cited 2018 Feb 27]. https://www.fda.gov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/ApprovedProducts/Ucm093833.htm.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services. Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger, United States, 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/child/0-18yrs-child-combined-schedule.pdf.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Silver Spring (MD): US Food and Drug Administration. SCOGS (Select Committee on GRAS Substances); [cited 2018 Aug 16]. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=SCOGS.
- Priest ND. The biological behavior and bioavailability of aluminum in man, with special reference to studies employing aluminum-26 as a tracer: review and study update. J Environ Monit. 2004; 6: 376,392.
- Poole RL, Pieroni KP, Gaskari S, Dixon TK, Park KT, Kerner JA. Aluminum in pediatric parenteral nutrition products: measured versus labeled content. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2011; 16 (2): 92-7.
- Sedman A. Aluminum toxicity in childhood. Pediatr Nephrol. 1992 Jul; 6 (4): 383-93.
- US Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. Rules and regulations. Fed Regist. 2003 Jun; 68 (100): 34286.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services. National Center for Health Statistics: Data table for boys length-for-age and weight-for-age charts; [cited 2019 April 2]. https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/who/boys_length_weight.htm.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services. National Center for Health Statistics: Data table for girls length-for-age and weight-for-age charts; [cited 2019 April 2]. https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/who/girls_length_weight.htm.
- US Food and Drug Administration, Department of Health and Human Services. Revision of the requirements for constituent materials. Final rule. Fed Regist. 2011 Apr 13; 76 (71): 20513-8.
- Office of the Federal Register, National Archives and Records Service, General Services Administration. Rules and regulations. Fed Regist. 1968 Jan; 33 (6): 369.
- Mitkus RJ, King DB, Hess MA, Forshee RA, Walderhaug MO. Updated aluminum pharmacokinetics following infant exposures through diet and vaccination. Vaccine. 2011 Nov 28; 29 (51): 9538-43.
- Miller S, Physicians for Informed Consent. Erratum in 'Updated aluminum pharmacokinetics following infant exposures through diet and vaccination.' In: ResearchGate. Berlin (Germany): ResearchGate GmbH; 2020 Mar 6 [cited 2020 Mar 6]. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/51718934_Updated_Aluminum_pharmacokinetics_following_infant_exposures_through_diet_and_vaccines/comments.
- Physicians for Informed Consent. Newport Beach (CA): Physicians for Informed Consent. Erratum in 'Updated aluminum pharmacokinetics following infant exposures through diet and vaccination'; [cited 2020 Mar 6]. https://physiciansforinformedconsent.org/mitkus-2011-erratum/.
- Flarend RE, Hem SL, White JL, Elmore D, Suckow MA, Rudy AC, Dandashli EA. In vivo absorption of aluminum-containing vaccine adjuvants using 26Al. Vaccine 1997 Aug-Sept; 15 (12-13): 1314-8.
- Verdier F, Burnett R, Michelet-Habchi C, Moretto P, Fievet-Groyne F, Sauzeat E. Aluminum assay and evaluation of the local reaction at several time points after intramuscular administration of aluminum containing vaccines in the Cynomolgus monkey. Vaccine. 2005 Feb 3; 23 (11): 1359-67.
- Weisser K, Göen T, Oduro JD, Wangorsch G, Hanschmann KO, Keller-Stanislawski B. Aluminum in plasma and tissues after intramuscular injection of adjuvanted human vaccines in rats. Arch Toxicol. 2019 Oct; 93 (10): 2787-96.
- Masson JD, Crépeaux G, Authier FJ, Exley C, Gherardi RK. Critical analysis of reference studies on the toxicokinetics of aluminum-based adjuvants. J Inorg Biochem. 2018 Apr; 181: 87-95.
Article translated by Physicians for Informed Consent
According to the US CDC, problems that can arise after vaccination with 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13), 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23), and any other vaccines include:(1-2)
- Serious allergic reactions occurring within minutes to hours of vaccination.
- Severe shoulder pain limiting movement of the injected arm.
- Fainting or collapsing after vaccination. You may be advised to sit or lie down for about 15 minutes after the vaccination to avoid fainting and injury that could result from a fall. It is important to inform your doctor if you experience ringing in the ears, vision changes or dizziness after vaccination.
Side Effects of PCV13 Vaccine (Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine)
Adverse reactions following administration of PCV13 vary according to the dose of the series and the age of the recipient. In children, the most commonly reported reactions were irritability, drowsiness, loss of appetite, redness, pain, or swelling at the vaccine site, and mild to moderate fever.
Children who received PCV13 at the same time as inactivated flu vaccine were found to be at increased risk of febrile seizures.
In adults, redness, swelling and pain at the injection site, fatigue, fever, chills, headache and body aches have mainly been reported.(3)
Prevenar 13 (PCV13) adverse reactions reported in infants and children during pre-approval clinical studies:(4) injection site pain, swelling, redness, fever, decreased appetite, increased and decreased sleep, irritability, diarrhoea, vomiting, rash, hives, hypersensitivity reaction including bronchospasm, swollen face and shortness of breath, seizures, pneumonia, gastroenteritis, bronchiolitis, death (reported as SIDS).
Prevenar 13 (PCV13) adverse reactions reported in adults during pre-approval clinical studies:(5) pain, swelling and redness at the injection site, restriction of arm movement, fever, vomiting, chills, muscle aches, fatigue, headache, decreased appetite, rash, joint pain, death (deaths reported in pre- approval included deaths from cancer, heart disease, peritonitis, Mycobacterium avium complex lung infection, and septic shock).
Prevenar 13 (PCV13) adverse reactions reported post-marketing:(6) Cyanosis, injection site lymphadenopathy, anaphylaxis, shock, hypotonia, pallor, apnea, angioneurotic oedema, erythema multiforme, injection site pruritus, urticaria, and rash.
Pre-approval clinical trials of the first pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, Prevenar (PCV7)compared the safety of Prevenar (PCV7) to an investigational meningitis C vaccine, seriously undermining the scientific validity of the trial.
In pre-authorisation clinical studies of Prevenar (PCV7), children in the groups receiving the pneumococcal vaccine suffered more from seizures, irritability, high fever and other reactions. There were 7 deaths in the Prevenar group (PCV12), including 5 deaths from sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). No long-term studies have been completed to evaluate whether Prevenar vaccine (PCV7), given alone or in combination with other vaccines, has an association with chronic disease or disability, such as the development of diabetes, asthma, seizure disorder, difficulty of learning, ADHD.(7)
Pre-approval safety trials of Prevenar 13 (PCV13) compared this next-generation vaccine with the original Prevenar vaccine (PCV7), a vaccine inadequately studied for safety, and concerns were reported in 2012 about a link between febrile seizures and Prevenar 13 (PCV13).(8-9)
PCV13 was associated with an elevated risk of febrile seizures when administered independently(10) and when given in combination with parenterally inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV).(11)
Some studies have also linked the PCV vaccine to Guillain-Barre syndrome,(12) to polyserositis,(13) to the septic shoulder(14) and erythema multiforme.(15)
Side effects of PPSV23 vaccine (Pneumococcus polysaccharide)
According to the CDC, about 50 percent of people who receive the pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) experience pain and redness at the injection site. Body aches, fever and more severe local reactions can also occur after administration of PPSV23.(16)
Adverse reactions of PNEUMOVAX23 (PPSV23) reported in adults during pre-approval US clinical trials:(17) injection site pain, redness, itching, bruising and swelling, headache, chills, fever, diarrhea, dyspepsia, nausea, upper respiratory tract infection, back pain, neck pain, pharyngitis, muscle pain, fatigue, depression, colitis ulcer, chest pain, angina pectoris, heart failure, tremor, rigors, sweating, stroke, lumbar radiculopathy, pancreatitis, myocardial infarction, death.
Nearly 80% of subjects participating in the pre-approval clinical studies experienced an injection site adverse reaction following revaccination three to five years after the initial vaccine. The rate of systemic adverse reactions (headache, fatigue, myalgia) following revaccination with PPSV23 was also higher, with 33% of adults 65 years of age and older and 37,5% of adults aged 50 years and older. between 64 and XNUMX years who reported an adverse reaction.(18)
Adverse Reactions of PNEUMOVAX23 (PPSV23) Reported Post-Marketing:(19) Anaphylactoid reactions, serum sickness, angioneurotic oedema, arthritis, arthralgia, vomiting, nausea, decreased mobility of extremities, edema peripheral in injected limb, fever, malaise, cellulitis, injection site warmth, lymphadenopathy , lymphadenitis, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia in patients with stable idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, haemolytic anemia in patients who have had other haematological disorders, paraesthesia, Guillain-Barré syndrome, radiculoneuropathy, febrile convulsions, rash, erythema multiforme, urticaria, cellulitis-like reactions.
Although PNEUMOVAX23 (PPSV23) is approved for use in children two years of age and older with conditions such as chronic heart and lung disease, diabetes, cochlear implants, CSF leaks, sickle cell disease, functional or anatomical asplenia, and immunosuppression, no information on the safety or efficacy of the vaccine in children is available from the vaccine package insert.(20)
Some studies have linked PPSV23 to systemic inflammatory reactions(21) and fever.(22-23-24-25-26)
References (click to open)
- CDC Pneumococcal Conjugate (PCV13) VIS. Nov. 5, 2015
- CDC Pneumococcal Polysaccharide VIS. Apr. 24, 2015
- CDC Pneumococcal Conjugate (PCV13) VIS. Nov. 5, 2015
- FDA Prevnar 13 Package Insert Aug. 22, 2017
- Ibid
- Ibid
- FDA Pneumococcal 7-Valent Conjugate Vaccine (PREVNAR) - Product Manufacturer Insert. October 1, 2002
- Hitt, E Prevnar 13 Should Be Watched for Febrile Seizure Risk, FDA Panel Says. medscape. Jan 31, 2012
- Tse A, Tseng HF, Greene SK, et al. Signal identification and evaluation for risk of febrile seizures in children following trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine in the Vaccine Safety Datalink Project, 2010-2011. Vaccine. 2012 Mar 2;30(11):2024-31
- Baker M, Jankosky C, Yih K, et al. The Risk of Febrile Seizures Following Influenza and 13-Valent Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccines. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2017 Fall; 4(Suppl 1): S464–S465.
- CDC Childhood Vaccines and Febrile Seizures Jun. 20, 2016
- Ravishankar, N Guillain-Barre Syndrome Following PCV Vaccine. J Neurol Neurosurg 4 (1): 134
- Tawfik P, Elie Gertner E, McEvoy CE Severe polyserositis induced by the 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine: a case report J Med Case Rep. 2017; 11: 142.
- DeRogatis MJ, Parameswaran L, Lee P, et al. Septic Shoulder Joint After Pneumococcal Vaccination Requiring Surgical Debridement. HSS J 2018 Oct;14(3):299-301
- Monastirli A, Pasmatzi E, Badavanis G et al. Erythema multiforme following pneumococcal vaccination. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2017 Mar;26(1):25-26.
- CDC Pneumococcal Polysaccharide VIS. Apr. 24, 2015
- FDA Pneumovax 23 - Pneumococcal Vaccine, Polyvalent. Package Insert Dec 30, 2014
- Ibid
- Ibid
- Ibid
- von Elten, KA, Duran LL, Banks TA, et al. Systemic inflammatory reaction after pneumococcal vaccine A case series Hum Vaccine Immunother. 2014 Jun 1; 10(6): 1767–1770.
- Huang DT, Chiu NC, Chi H, et al. Protracted fever with cellulitis-like reaction in pneumococcal polysaccharide-vaccinated children. Pediatric Infect Dis J. 2008 Oct;27(10):937-9.
- Yousef E, Mannan S. Systemic reaction to pneumococcal vaccine: how common in pediatrics? Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008 Jul-Aug;29(4):397-9
- Gabor EP, Seeman M. Acute febrile systemic reaction to polyvalent pneumococcal vaccine. JAMA. 1979 Nov 16;242(20):2208-9.
- Hasan S, Yousef M, Shridharani S Severe febrile systemic reaction to pneumococcal vaccine. J Natl Med Assoc. 2005 Feb; 97(2): 284–285.
- Lee A, Goyal R, Shan HY. Severe protracted fever following pneumococcal vaccine. Am J Med Sci. 2006 Dec;332(6):351-3.
This article is summarized and translated by National Vaccine Information Center.

